Name plate of a machine is very important. It tells about the working characteristics & safe limits of the machine. Name plate also provides details of the manufacturer along with its serial number.
In this post, We are going to discuss the name plate of transformer.
There are many types of transformers like Step up & step down transformers, power transformers, distribution transformers, instrumental transformers & Special purpose transformers. By name plate of transformer we can easily distinguish the transformer.
Before name plate of the transformer, we should study the transformer first.
Transformer
Transformer is a static Electrical machine which carry no rotating part. Transformer transfer electrical power from one circuit to another circuit at same frequency.
Transformer works on the principle of faraday law of mutual induction. Generally, there are two windings in transformer, Primary winding & secondary winding. Both the windings are separated from each other & no electrical link exist between both the windings Accept a changing magnetic field links both the windings with common silicon steel stamping.
Power always remain the same on both the sides of the transformer. It is the voltage & current which varies on both the sides of the transformer As explained below.
For Example:
A 300kVA Distribution transformer with voltage ratio 11kV/415V.
Primary Voltage=11000
Primary Current= 15.75
Apparent Power Primary= √3 *11000*15.75= 300077.8
Secondary Voltage=433
Secondary Current=400
Apparent Power Secondary= √3*433*400= 299991.2
 |
| Distribution Transformers(1) |
Why do we need transformers ?
Reason 1. To change the Voltage level
Since power generating stations are at remote places far away from consumers. This distance may be in thousands of kilometers. If we send generated voltage directly to the feeder line through that much long distance than this power drops down in the way, totally. Because power loss is equal to I²R. When voltage is low, Current is high Which makes the power loss high.
That's why to transfer power, voltage should be higher at Generating station. To step up the voltage, we need step-up transformer.
Now, at consumer end; we need low voltage. That's why there is need to step down the voltage. At this stage, we need a step down transformer.
Now the question is Why are we using transformer to change the voltage ?
Answer is, Transformers are static machines without any moving part, with less losses. Makes the transformer the most efficient device to change the voltage. That's Why used widely.
Reason 2. Instrumentation
Since high voltage & high current can not be measured directly. We need instrument transformers which convert high voltage & high current to low measurable level, directly.
Since high voltage & high current can not be measured directly. We need instrument transformers which convert high voltage & high current to low measurable level, directly.
Reason 3. For Special purposes
There are some transformers which are made for special purposes like an Auto transformers which provide variable voltage by just rotating its variac.
Name Plate of Transformer
Lots of details are mentioned on transformer's name plate depending upon the type of transformer whether it is power transformer, distribution transformer, instrumental transformer or special purpose transformer .
In this post we will discuss the name plate of 300KVA distribution transformer having a voltage ratio of 11kV/415V.
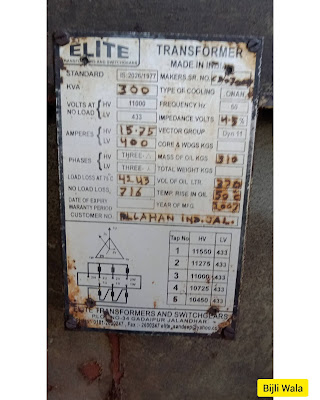 |
| 300 KVA, 11KV/415V, DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMER (2) |
List of transformer attributes given below
1. Manufacturer's name-address & serial number of transformer
Manufacturer details are always given at front. As shown in an image above; transformer makers are Elite transformer from Jalandhar, Punjab.
2. Rating
Transformer rating is 300 KVA. Transformers are rated in kVA (APPARENT POWER) Not in kW, Because transformers are power transforming device that transfer power from one circuit to another. Transformers are not power consumers.
3phase Real power =√3 V I cos¢
Where,
√3VI= Apparent power (Voltage ×Amperes(VA))
√3VIcos¢= Real power (Watt)
It means if cos¢ is eliminated from real power than it becomes apparent power (VA)
The term cos¢ known as power factor.
If load is inductive than power factor is lagging. If load is capacitive than power factor is leading. The value of power factor varies from 0 to 1 which is fully depend upon the type of load which is connected across the transformer's secondary. It means power factor is load dependent.
Since, transformer has no link with the power factor that's why transformers are rated in KVA rather than KW.
3. Voltage on HV & LV side
Both the sides HV and LV side voltages are mentioned in this parameter. In general, distribution transformer shown above HV voltage is 11KV & LV voltage is 415 Volts.
4. Rated Current
It is the safe level of rated working current; under some specified condition; under which machine works precisely without overheating & excessive 'Mechanical & Electrical' stress.
As shown in an image
HV current= 15.75 Amps
LV current= 400 Amps
5. Winding connections
It tells about the connection type of the winding whether it is star or delta on both the winding sides. In distribution transformer above, primary is delta & secondary in star. Because we need neutral at secondary side for single phase connections.
6. No load loss
It is the value of core loss occurring in open circuit or at no load conditions.
In our name plate no load loss=716 Watt.(see image )
7. Load loss
It is the value of copper loss occurring in the winding under the full load conditions at some specified temperature,
In our name plate load loss at 75°C is 4243 Watt.(see image )
8. Type of cooling
This term tell about the type of cooling. In an image above, Transformer is ONAN type which means oil & air both are cooled naturally.
ONAN stands for- oil natural air natural
In ONAN system hot oil continuously rotate in fins without any external force & a Natural air passes through fins naturally.
There are much more types of cooling but all these types depend upon the rating & type of transformer.
For example;
ONAF- Oil natural air forced
In this system oil naturally flow through the fins but air is forced with the cooling fan.
OFAF- Oil forced air forced
In this type, oil flows with the help of pump & air is blown with cooling fan.
9. Frequency
The frequency remains constant on both the sides of transformer. In India, frequency standard is 50Hz+-3%.
10. Impedance volts
It generally listed in percentage which tells about the voltage drop in transformer under short circuit conditions.
This value also tell about highest current flow when transformer get short circuited.
The formula of short circuit current= (100/impedance volts)× full load rated current.
In an image; impedance volts is 4.3%
which mean short circuit current is; [(100/4.3)*300]= 6976.7 Amps
11. Vector Grouping
This term is the standard set by international Electrotechnical commission (IEC) which tells about the winding configuration on HV & LV side. This term generally tells about the phase shift between primary & secondary voltage.
For example
In Image, vector grouping is DYn11.
Since our transformer is distribution transformer. Primary HV winding is Delta & secondary LV winding is Star.
NOW
DYn11
D- Primary side which is Delta
Y- Secondary side which is wye or star
n- stands for neutral brought out on Secondary side
11- This terms shows the 30° lead in phase shift. LV phase leads the HV phase by 30°.
This 11 is taken off from clock Since in our clock of full circle there are total 12 numbers.
(1full circle = 360°)
One number in terms of degree equals to ;360°÷12= 30°
Since 11 is Infront of 12 in the left; that's why taken as 30° lead. LV winding leads HV by 30°.
12. Mass of oil in kgs
It is the total weight of transformer oil Which is 310 Kgs. (See image)
13. Total weight of transformer
Total weight of transformer includes transformer oil. As shown in image, total weight of 300kVA transformer is 1500KG.
14. Volume of oil (liters)
370 litres
15. Year of manufacturing
2007
I hope you like the post. If you have any query or suggestions, please do comments.
Your comments are valuable to us.
